Breast Milk Pumping
What is “pumping”?
Breast pumps can be used to remove milk from the breasts when a mother is unable to directly breast feed her baby. This could mean the inability to breastfeed baby directly or when the mother is not physically with baby and needs to remove milk from her breasts.
Using any kind of breast pump to remove milk from the breasts is considered “pumping”.
When to begin pumping:
We typically recommend that a mother does not begin pumping until her milk supply is well established, about 4-6 weeks after delivery. If the newborn is separated from mother or direct breast feeding is unsuccessful, the mother should begin pumping immediately.
A mother may also use an electric or hand pump to relieve breast pain associated with engorgement. When used for engorgement, stop pumping when the pain is relieved (<5 minutes) rather than pumping until the breasts are emptied.
Selecting a breast pump:
Breast pumps fall into 4 basic categories:
1) Hospital grade – use while establishing a milk supply
2) Personal use – for employed mothers at work
3) Battery or small electric – for employed mothers or for occasional use
4) Manual pumps – best used for occasional use. The two standard settings on a pump
Select a pump that meets the needs of you and your baby. Pumps can range in price from about $35 to over $300. Most health insurance companies now cover the cost of a breast pump so check with your specific plan and request a prescription from your provider as needed.
You may also want to consider the ease of use, portability, ease of cleaning, and durability when selecting a pump. Select a pump that has multiple flanges so you can adjust them to your comfort. It is useful if your electric pump can be plugged in and also could be operated on batteries at other times in case of travel or power outages.
Pumping:
Plan to use a breast pump the same number of times that the baby will be feeding while you are away or unable to feed your baby. Try to maintain a routine and avoid skipping or postponing pumping. When you skip pumping you will begin to see a decrease in your supply.
Assure that your flange size is appropriate. The nipple should move freely in and out during the suction cycle. The areola should not move into the flange. You should not have a white ring around the areola.
Start the pump suction on low and gradually increase the suction to the maximum setting that is comfortable to you. Too much suction can collapse your milk ducts and result in poor milk emptying.
Start in a “let-down” phase with faster cycles. When you begin to see the let-down reflex (time when the milk is flowing faster) decrease the cycle speed.
Pump for 2-3 minutes after the last drops of milk or a maximum of 30 minutes. During this time you should have 2-3 let-down reflexes. If you do not have much time, a short session is better than skipping a pumping.
For information about hands-on pumping watch this video:
Returning to work:
Talk to your employer about a private, clean space where you can pump. You may want to do a “practice run”, timing how long it takes to travel, locating where you can store your milk, and using your breast pump.
Pump regularly while away from baby (at the same times that baby would typically nurse) and breastfeed when you are home. If you see a decrease in your supply, breastfeed on your days off and add extra pumping sessions if you have time.
For more, check out our Breastfeeding and Returning to Work article by one of our lactation consultants.

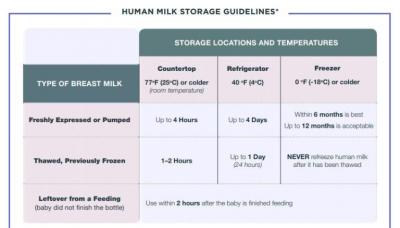
Storage of breast milk:
Chill any milk that you pump at work in a refrigerator. A cooler bag can be used to transport the milk home.
The guidelines for storage of breast milk can be found at:
https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/recommendations/handling_breastmilk.htm
If you have more questions or concerns about breastfeeding or pumping, schedule a specific appointment with one of our lactation consultants. Call 410-263-6363 to make an appointment. Bring your baby and your pump with you.
You can also attend our free Breastfeeding Support Group (for Annapolis Pediatrics patients only) to talk with a lactation consultant and other mothers at the same stage in life or attend our Breastfeeding Adventures class (for expectant and new parents).
Register to attend a class on our website events page at: https://annapolispediatrics.com/events
